Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
Li, S.; Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.; Deng, D.*
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/07
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-036, 115 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to investigate the environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris from the viewpoints of materials science. The research objective is cracking behavior in fuel debris which is presumed to be influenced by environment during long-term fuel debris processing period. The degradation models will be established to simulate the oxidation and hydrogenation processes possibly occurred at fuel debris. The evolution of phase constitution and the corresponding property change in the simulated fuel debris under various environmental conditions …
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2021-058, 75 Pages, 2022/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the environment induced property change and cracking behavior in fuel debris from the viewpoints of materials science. The research objective is cracking behavior in fuel debris which is presumed to be influenced by environment during long-term fuel debris processing period. The degradation models will be established to simulate the oxidation and hydrogenation processes possibly occurred at fuel debris.
Oda, Chie; Kawama, Daisuke*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Benbow, S. J.*; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 19(10), p.1075 - 1087, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Construction & Building Technology)Concrete in a transuranic (TRU) waste repository is considered a suitable material to ensure safety, provide structural integrity and retard radionuclide migration after the waste containers fail. In the current study, coupling between chemical, mass-transport and mechanical, so-called non-linear processes that control concrete degradation and crack development were investigated by coupled numerical models. Application of such coupled numerical models allows identification of the dominant non-linear processes that will control long-term concrete degradation and crack development in a TRU waste repository.
Hayashi, Makoto*; Shobu, Takahisa
Residual Stress, p.100 - 132, 2021/00
Structural materials may undergo fatigue fracture or stress corrosion cracking during use. One of the causes is the residual stress generated by heat treatment and processing in the manufacturing process of structural materials. There are various methods for measuring the residual stress. This book introduces measurement techniques using ultrasonic and magnetic methods, starting with laboratory X-rays, synchrotron radiation X-rays, and neutrons. In addition, we will outline examples of measurement of residual stress due to processing and welding of various materials, measurement examples of actual machines, change behavior of residual stress due to static and repeated loads, and evaluation methods of fatigue remaining life based on the change behavior.
Igarashi, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2020-006, 261 Pages, 2020/09
A literature review was conducted on the increase in surface area of vitrified products of HLW due to the fracturing caused by cooling during glass pouring process and by mechanical impact, from the perspective of a parameter of the radionuclide release model in the performance assessment of geological disposal system studied overseas. The review was focused on the value of surface area increase factor set as a parameter in the model, the experimental work to evaluate an increase in surface area, and how the parameters on surface area were determined based on the experimental results. The surface area obtained from the experiments executed in Japan was also discussed in comparison with the overseas studies. On the basis of the investigation, the effects of various conditions on the surface area were studied, such as a diameter of vitrified product, cooling condition during and after the glass pouring, impact on vitrified products during their handling, environment after the closure of disposal facility, and others. The causes of fracturing are associated with the phenomena or events in the waste management process such as production, transport, storage, and disposal. The surface area increase factors set in the nuclide release model of the glass and their bases were reviewed. In addition, the measured values and the experimental methods for surface increase factors published so far were compared. Accordingly, the methods for measuring surface area as the bases were identified for these factors set in the models. The causes of fracturing and features of these factors were studied with respect to the relation with the waste management process. The results from the review and assessment can contribute to the expanding the knowledge for the conservative and realistic application of these factors to performance assessment, and to the developing and upgrading of safety case as a consequence.
Kato, Chiaki; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1371 - 1379, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of crystal textures and the potentials in the anodic oxidation of zirconium in a boiling nitric acid solution were investigated to study the stress corrosion cracking of zirconium in nitric acid solutions. The growth of the zirconium oxide film dramatically changed depending on the applied potential at a closed depassivation potential (1.47 V vs. SSE). At 1.5 V, the zirconium oxide film rapidly grows, and its growth exhibits cyclic oxidation kinetics in accordance with a nearly cubic rate law. The zirconium oxide film grows according to the quantity of electric charge, and the growth rate does not depend on the crystal texture in the pretransition region before the cyclic oxidation kinetics. However, the growth and cracking under the thick oxide film depend on the crystal texture in the transition region. On the normal direction side, the oxide film thickness decreases on average since some areas of the thick oxide film are separated from the specimen surface owing to the cracks in the thick oxide. On the rolling direction side, cracks are found under the thick oxide film, which deeply propagate along the RD without an external stress. The cracks under the thick oxide film propagate to the center of the oxide layer. The cracks in the oxide layer propagate in the (0002)Zr plane in the zirconium matrix. The oxide layer consists of string-like zirconium oxide and zirconium hydride. The string-like zirconium oxide contains orthorhombic ZrO in addition to monoclinic ZrO
in addition to monoclinic ZrO . As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO
. As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO to monoclinic ZrO
to monoclinic ZrO in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Okada, Hiroshi*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(5), p.051207_1 - 051207_8, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.14(Engineering, Mechanical)A number of surface cracks with large aspect ratio have been detected in components of nuclear power plants in recent years. The depths of these cracks are even larger than the half of crack lengths. However, the solutions of the stress intensity factor were not provided for semi-elliptical surface cracks with large aspect ratio in the current fitness-for-service codes. In this study, in order to conduct integrity assessment for cracked components, the solutions of the stress intensity factor were calculated using finite element analysis for semi-elliptical surface cracks with large aspect ratio in plates. Solutions were provided at both the deepest and the surface points of the surface cracks. Some of solutions were compared with the available existing results. As the result, it was concluded that the solutions proposed in this paper are applicable in engineering applications.
Minehara, Eisuke
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 557(1), p.16 - 22, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAERI FEL facility at Tokai, Ibaraki, Japan has been well known one of the two existing and operating superconducting energy recovery linacs together with one more of JLAB (Jefferson national accelerator facility) FEL facility at Newport News, Virginia, U.S.A. We have independently and successfully developed one of the most advanced and newest accelerator technologies named "superconducting energy recovery linacs (ERLs)" and the application technologies using ERLs in future. We plan to report the current high power FEL upgrade program research, stress corrosion cracking prevention technology research, large current and high brightness photoelectron gun research of negative-electron affinity (NEA) photocathode and NEA electron-excitation cathode as the most important elemental technology in realizing many powerful ERLs.
Sugino, Hideharu*; Ito, Hiroto*; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.233 - 241, 2005/12
The purpose of this research is to establish the reliability evaluation method of aged nuclear power components for seismic events from a viewpoint of long-term use of the existing light water reactor nuclear power plants. For this purpose, we developed a piping failure probability evaluation code "PASCAL-SC" based on probabilistic fracture mechanics, and a probabilistic seismic hazard evaluation code "SHEAT-FM" for calculating the seismic occurrence probability of a plant site, paying attention to aging such as fatigue crack progress by the stress corrosion cracking and seismic load in primary coolant piping system. We proposed the reliability evaluation method of aged piping for seismic events by combination of these codes. Using this method, we evaluated the reliability of a weld line in the PLR(Primary Loop Recirculation system) piping of the BWR model plant for seismic events.
Shibata, Katsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; Li, Y.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2005 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.299 - 300, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of KNS-AESJ Joint Summer School 2005 for Students and Young Researchers, 2, p.221 - 228, 2005/08
For core internals, the main research items are intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) of low carbon stainless steel in core shrouds and primary loop recirculation pipes in boiling water reactor (BWR), and irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) which is caused by the synergistic effects of neutron and gamma-ray radiation, corrosion by high temperature water, and the residual and/or applied stresses. This paper describes the current status and typical results of fundamental study for mechanistic understanding of IGSCC and IASCC, development of IASCC evaluation technology for BWR plants based on post-irradiation IASCC test data as a part of METI's national project, in-pile IASCC tests.
Minehara, Eisuke; Hajima, Ryoichi; Iijima, Hokuto; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Nagai, Ryoji; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Nishitani, Tomohiro; Sawamura, Masaru; Yamauchi, Toshihiko
Proceedings of 27th International Free Electron Laser Conference (FEL 2005) (CD-ROM), p.305 - 308, 2005/00
The JAERI high power ERL-FEL has been extended to the more powerful and efficient free-electron laser (FEL) than 10kW for nuclear energy industries, and other heavy industries like defense, shipbuilding, chemical industries, environmental sciences, space-debris, and power beaming and so on. In order to realize such a tunable, highly-efficient, high average power, high peak power and ultra-short pulse FEL, we need the efficient and powerful FEL driven by the JAERI compact, stand-alone and zero boil-off super-conducting RF linac with an energy-recovery geometry. Our discussions on the ERL-FEL will cover the current status of the 10kW upgrading and its applications of non-thermal peeling, cutting, and drilling to decommission the nuclear power plants, and to demonstrate successfully the proof of principle prevention of cold-worked stress-corrosion cracking failures in nuclear power reactors under routine operation using small cubic low-Carbon stainless steel samples.
Amaya, Masaki; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(11), p.1091 - 1099, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Effect of absorbed hydrogen on the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility of unirradiated Zircaloy cladding was examined. The data obtained from literatures show that the ratios of SCC threshold stress (
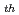 ) to 0.2% yield stress (
) to 0.2% yield stress (
 ) in unirradiated Zircaloy claddings increase with increasing hydrogen contents below 60 ppm, irrespective of the kind of Zircaloy-2 and -4. Thermodynamic calculations were carried out for the reaction between iodine gas and zirconium containing hydrogen. The results suggested that the reactions hardly occurred at increased hydrogen content and zirconium reacted with iodine gas only below 90 ppm of hydrogen. Since these tendencies correspond to those of the ratios of
) in unirradiated Zircaloy claddings increase with increasing hydrogen contents below 60 ppm, irrespective of the kind of Zircaloy-2 and -4. Thermodynamic calculations were carried out for the reaction between iodine gas and zirconium containing hydrogen. The results suggested that the reactions hardly occurred at increased hydrogen content and zirconium reacted with iodine gas only below 90 ppm of hydrogen. Since these tendencies correspond to those of the ratios of 
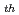 to
to 
 on the hydrogen content, it is considered that hydrogen affects the reactions between iodine gas and zirconium and reduces the SCC susceptibility of Zircaloy claddings.
on the hydrogen content, it is considered that hydrogen affects the reactions between iodine gas and zirconium and reduces the SCC susceptibility of Zircaloy claddings.
Nakano, Junichi; Miwa, Yukio; Koya, Toshio; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.643 - 647, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:48.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To study effects of minor elements on the irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC), high purity Type 304 and 316 stainless steels (SSs) were fabricated and added minor elements, Si or C. After neutron irradiation to 3.5 10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1MeV), the slow strain rate tests (SSRT) for the irradiated specimens was conducted in oxygeneted high purity water at 561 K. Fracture surface of the specimens was examined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) after the SSRT. Fraction of intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) on the fracture surface after the SSRT increased with netron fluence. Suppression of irradiation hardening and increase of peiod to SCC fracture as benefitical effects of the additional elements, Si or Mo, were not observed obviously. In high purity SS added C, fraction of IGSCC was the smallest in the all SSs, although irraidiation hardening level was the largest in the all SSs. Addition of C suppressed the susceptibility to IGSCC.
1MeV), the slow strain rate tests (SSRT) for the irradiated specimens was conducted in oxygeneted high purity water at 561 K. Fracture surface of the specimens was examined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) after the SSRT. Fraction of intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) on the fracture surface after the SSRT increased with netron fluence. Suppression of irradiation hardening and increase of peiod to SCC fracture as benefitical effects of the additional elements, Si or Mo, were not observed obviously. In high purity SS added C, fraction of IGSCC was the smallest in the all SSs, although irraidiation hardening level was the largest in the all SSs. Addition of C suppressed the susceptibility to IGSCC.
The Working Team for Examination Operation of Samples From Core Shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Unit-3
JAERI-Tech 2004-044, 92 Pages, 2004/05
The present examination has been performed with the objective to ensure the transparency of the examination as the third-party organization by providing technical basis for identifying the causes of cracking through examination of the sample taken from the cracked region of outer H6a welding portion of the core shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Station Unit-3, which was a part of sample stored in the Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., Ltd. in the examination of Tokyo Electric Power Company in 2001. The present examination of the sample was conducted at the post irradiation examination facilities of JAERI. The following findings were obtained from the result of the present examination. (1)Three cracks were observed at the portion 3 to 9mm apart from the weld metal and the maximum depth was about 8mm. (2)Intergranular cracking was observed in almost whole fracture surface. The transgranular cracking was partially observed within the depth of about 300 m from the surface. (3)Hardening layer over Hv400 at its maximum was found from the surface to the depth of about 500
m from the surface. (3)Hardening layer over Hv400 at its maximum was found from the surface to the depth of about 500 m. Based on the examination results concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant, it is concluded that the cracks were mainly initiated in the hardening layer by transgranular stress corrosion cracking and propagated along the grain boundaries.
m. Based on the examination results concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant, it is concluded that the cracks were mainly initiated in the hardening layer by transgranular stress corrosion cracking and propagated along the grain boundaries.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi; Nakajima, Hajime*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Suzuki, Masahide; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Nakano, Junichi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2004-015, 114 Pages, 2004/03
The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) visually inspected the weld joint of core shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Station Unit-2 by a direction of the Nuclear and Industrial Agency, cracks were observed at outer side of the ring weld joint (H3) between a core shroud middle trunk and a middle ring. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co. Ltd. (NFD) on the specimen including cracks sampled from the core shroud. The present examination has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD from the planning stage. Based on results of the present examination, the probable presence of tensile residual stress by welding process and dissolved oxygen contents in the cooling water, it was shown that the cracks were considered to be stress corrosion cracking (SCC). However, the cause of the cracks needs more consideration on the way of shroud construction.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi
JAERI-Tech 2004-012, 62 Pages, 2004/02
At Onagawa Nuclear Power Station Unit-1 of the Tohoku Electric Power co., inc., cracks were confirmed near welded joints of core shroud in 15th periodical inspection. Tohoku Electric Power co., inc. has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., Ltd.. To investigate independently, a JAERI's own evaluation report was provided. The results are as follows; (1) Hardening layer was detected at the depth of about 150-250 m from outer surface of the sample. (2) Corrosion products were observed on inner surface of the cracks and some of them penetrated into grains. (3) Transgranular cracking and intergranular cracking were observed at the region within about 100
m from outer surface of the sample. (2) Corrosion products were observed on inner surface of the cracks and some of them penetrated into grains. (3) Transgranular cracking and intergranular cracking were observed at the region within about 100 m and the deeper region more than about 200
m and the deeper region more than about 200 m in depth from outer surface of the sample, respectively. (4) Distinct chromium depletion was not detected at the grain boundaries. (5) Chemical compositions of the sample corresponded to type 304L stainless steel in Japanese Industrial Standard. From the above, it is concluded that the cracks are stress corrosion cracking.
m in depth from outer surface of the sample, respectively. (4) Distinct chromium depletion was not detected at the grain boundaries. (5) Chemical compositions of the sample corresponded to type 304L stainless steel in Japanese Industrial Standard. From the above, it is concluded that the cracks are stress corrosion cracking.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi
JAERI-Tech 2004-011, 64 Pages, 2004/02
At the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station Unit-1 of the TEPCO, cracks were confirmed at the weld joint (H4) in the middle of core shroud, by the visual inspection test for the weld joint of core shroud during the 13th periodic examination by a direction of the Nuclear and Industrial Agency. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with NFD on the specimen including cracks sampled from the core shroud. The present research has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD from the planning stage, receiving the final data given by the examination and providing JAERI's own evaluation report as a third-party organization for assuring the transparency. As a result, the consideration of residual stress induced with welding process and dissolved oxygen concentration in core cooling water, it was concluded that the cracks were initiated by SCC and propagated three-dimensionally through grains, and some cracks reached weld metal.